A Comprehensive Guide To Hot Die Forging
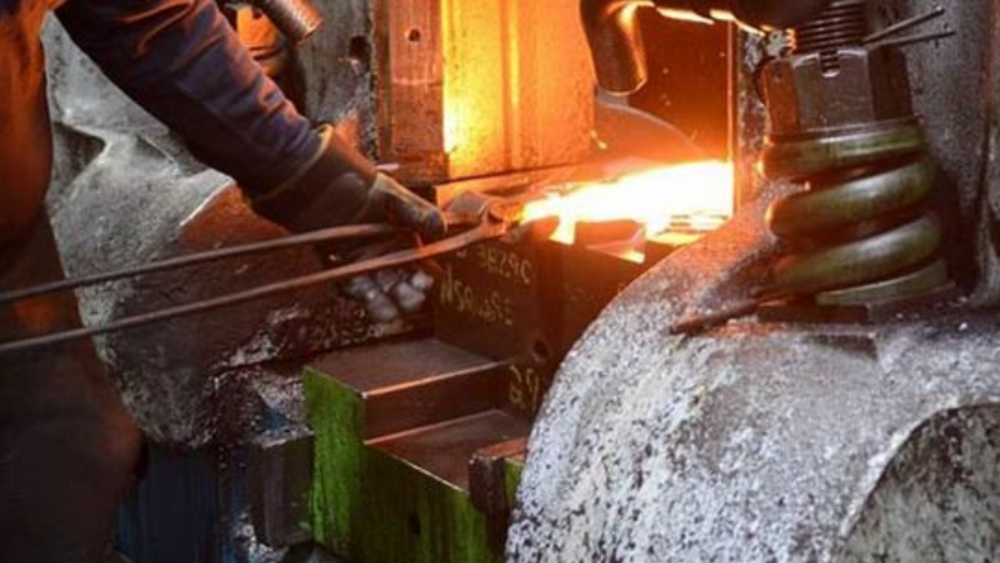
Making strong and long-lasting components for a variety of industries, hot die forging is at the forefront of metalworking techniques. Using specialized dies and high pressure, the metal is shaped during this precise and effective manufacturing process to make it malleable.
As a result, premium forged parts are produced that have improved mechanical characteristics, exceptional strength, and superior integrity. In this thorough overview of hot die forging Or custom forging, we will delve into the essentials of this tried-and-true process, examining its workings, uses, and importance in contemporary manufacturing.
The Hot Die Forging Process
Hot die forging is a forging process that operates at elevated temperatures, typically above the recrystallization temperature of the metal being forged. The process involves several essential steps:
Heating
The first step in hot die forging is heating the raw material to the appropriate temperature. The metal is heated in a furnace until it reaches the desired temperature, making it more malleable and ready for deformation.
Pre-forming
After heating, the preheated metal is placed on a die or anvil, where it is pre-formed into a shape resembling the final component. This pre-forming step ensures that the metal is ready for the subsequent forging process.
Forging
Once pre-formed, the metal is placed between two halves of a die. These dies have the negative shape of the desired final component. High-pressure hydraulic or mechanical presses then compress the metal between the dies, shaping it into the desired form.
Cooling and Trimming
After forging, the component is allowed to cool to room temperature. Trimming or cutting may be required to remove excess material or achieve the final dimensions.
Applications of Hot Die Forging
Hot die forging finds widespread applications across a range of industries, contributing to the production of critical components used in diverse sectors. Some notable applications include:
Automotive Industry
Hot die forging is extensively used in the automotive sector to manufacture components such as crankshafts, connecting rods, gear blanks, and suspension parts. These precision-forged components ensure the durability and performance of automotive systems, contributing to the safety and reliability of vehicles.
Aerospace and Aviation
In the aerospace and aviation industries, hot die forging plays a pivotal role in producing critical components, including turbine discs, compressor blades, and landing gear parts. The exceptional strength and integrity of hot die-forged parts make them ideal for withstanding the demanding conditions and stresses encountered in aviation applications.
Oil and Gas Exploration
Hot die forging is vital in the production of oil and gas exploration components, such as drill bits, flanges, and valves. These forged parts must withstand harsh operating environments, and the high quality and reliability of hot die forging ensure their suitability for these critical applications.
Industrial Machinery
In industrial machinery manufacturing, hot die forging is employed to produce components like gears, shafts, and bearings. These precision-forged parts are essential for ensuring the efficient and smooth operation of various machines and equipment.
Power Generation
Hot die forging is utilized in the power generation sector for producing components like turbine blades, steam turbine rotors, and generator shafts. These forged parts play a vital role in the efficient and reliable operation of power plants, contributing to the generation of electricity.
Significance of Hot Die Forging
Hot die forging holds immense significance in modern manufacturing due to its ability to produce high-quality components with exceptional mechanical properties. The process ensures precise shaping and dimensional accuracy, reducing the need for secondary machining operations and material wastage. This makes hot die forging an efficient and cost-effective manufacturing method, particularly for high-volume production.
Conclusion
As technology advances, hot die forging continues to evolve, with innovative techniques and materials enhancing its capabilities further. The process’s continued significance in the manufacturing landscape underscores its enduring value, ensuring that hot die forging remains an indispensable method in the realm of precision metal shaping for years to come.